Chilean version of the INECO Frontal Screening (IFS-Ch), Psychometric properties and diagnostic accuracy
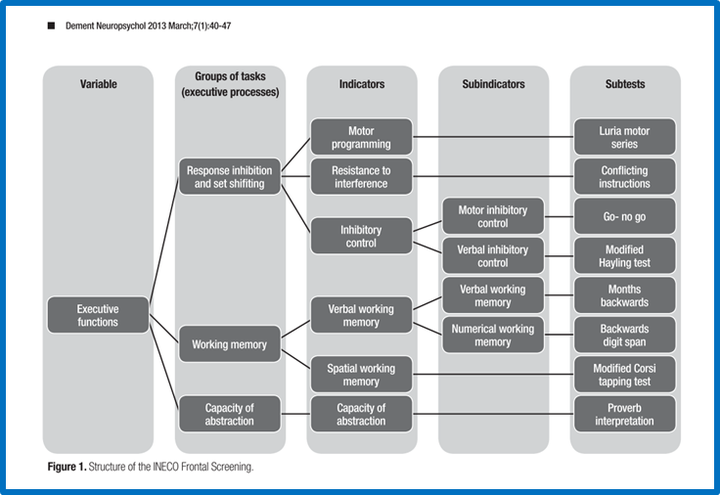 Caption by Josefina Ihnen
Caption by Josefina Ihnen
Abstract
Objective - This study sought to analyze the psychometric properties and diagnostic accuracy of the Chilean version of the INECO Frontal Screening (IFS-Ch) in a sample of dementia patients and control subjects. Methods - After adapting the instrument to the Chilean context and obtaining content validity evidence through expert consultation, the IFSCh was administered to 31 dementia patients and 30 control subjects together with other executive assessments (Frontal Assessment Battery [FAB], Modified version of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test [MCST], phonemic verbal fluencies [letters A and P] and semantic verbal fluency [animals]) and global cognitive efficiency tests (Mini mental State Examination [MMSE] and Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination-Revised [ACE-R]). Caregivers of dementia patients and proxies of control subjects were interviewed with instruments measuring dysexecutive symptoms (Dysexecutive Questionnaire [DEX]), dementia severity (Clinical Dementia Rating Scale [CDR]) and functional status in activities of daily living (Activities of Daily Living Scale [IADL] and Technology-Activities of Daily Living Questionnaire [T-ADLQ]). Convergent and discriminant validity, internal consistency reliability, cut-off points, sensitivity and specificity for the IFS-Ch were estimated. Results - Evidence of content validity was obtained. Evidence of convergent validity was also found showing significant correlations (p<0.05) between the IFS-Ch and the other instruments measuring - executive functions (FAB, r=0.935; categories achieved in the MCST, r=0.791; perseverative errors in the MCST, r= –0.617; animal verbal fluency, r=0.728; A verbal fluency, r=0.681; and P verbal fluency, r=0.783), dysexecutive symptoms in daily living (DEX, r= –0.494), dementia severity (CDR, r= –0.75) and functional status in activities of daily living (T-ADLQ, r= –0.745; IADL, r=0.717). Regarding reliability, a Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of 0.905 was obtained. For diagnostic accuracy, a cut-off point of 18 points (sensitivity=0.903; specificity=0.867) and an area under curve of 0.951 were estimated to distinguish between patients with dementia and control subjects. Discussion - The IFS-Ch showed acceptable psychometric properties, supported by evidence of validity and reliability for its use in the measurement of executive functions in patients with dementia. The diagnostic accuracy of the IFS-Ch for detecting dementia patients was also considered acceptable.